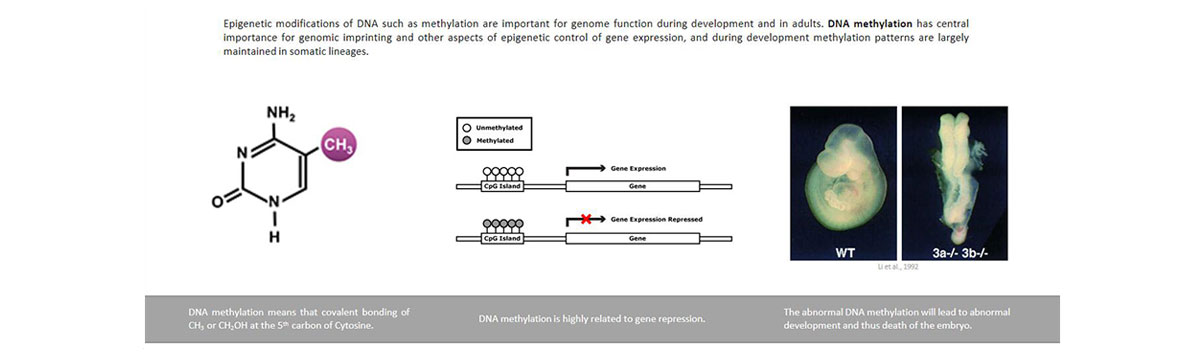
Genomic imprinting is a normal form of gene regulation that causes a subset of mammalian genes to be expressed from one of the two parental chromosomes. Some imprinted genes are expressed from the maternally inherited chromosomes and others from the paternally inherited chromosomes. The monoallelic parent of origin-specific expression of imprinted genes in mammals is regulated by differentially DNA methylated imprinting control regions (ICRs).
Imprinted gene diseases are mostly caused by abnormal DNA methylation in imprinting control regions. the disorders of imprinted gene can cause the defect of embryo development, brain function et.al.
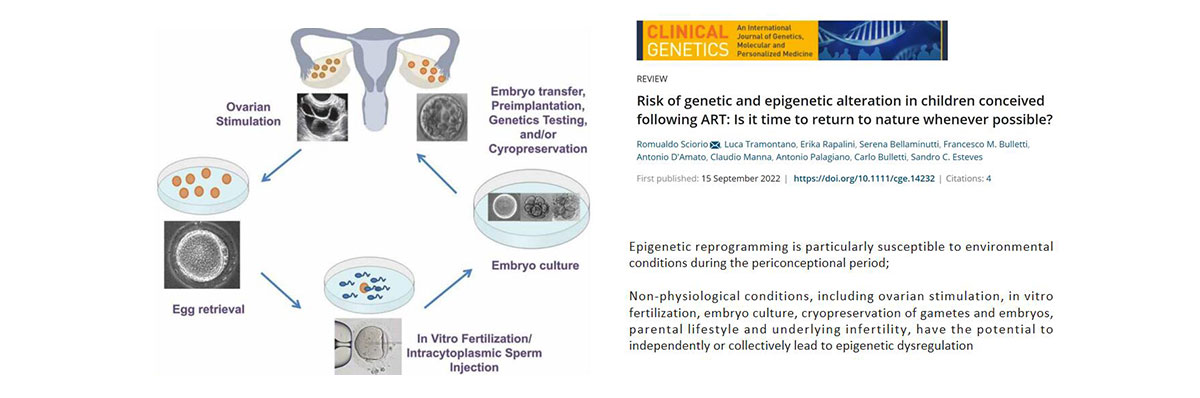
As French National Heath Data showed, incidence rate of imprinted gene disease was 1.4‰ for infants from normal conception and 3‰ for IVF infants. It was mostly caused by abnormal DNA methylation. However, there is no specific method to diagnose, screen or even cure the imprinted gene disease.